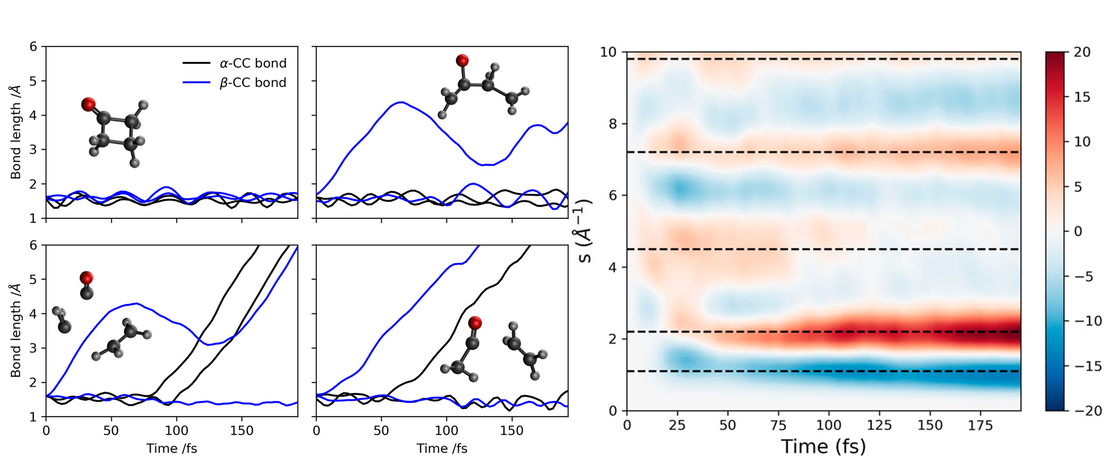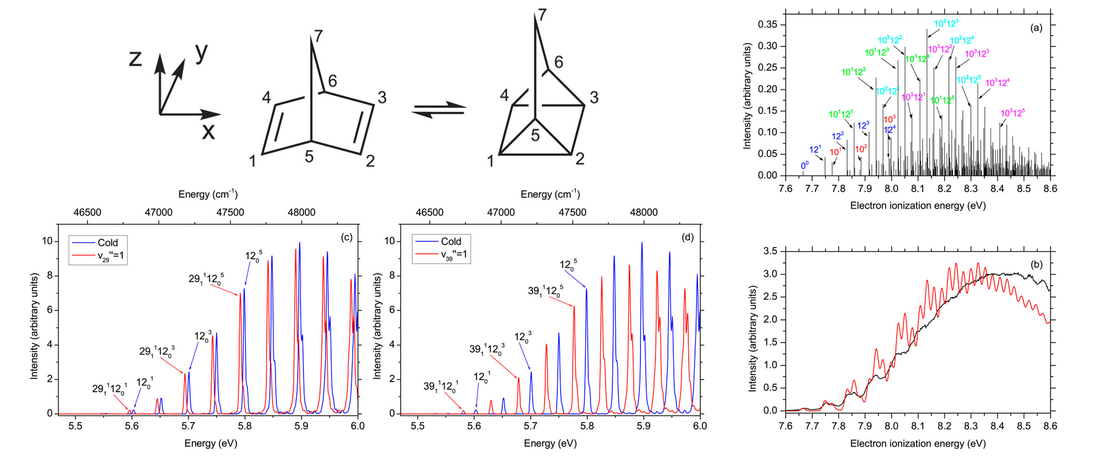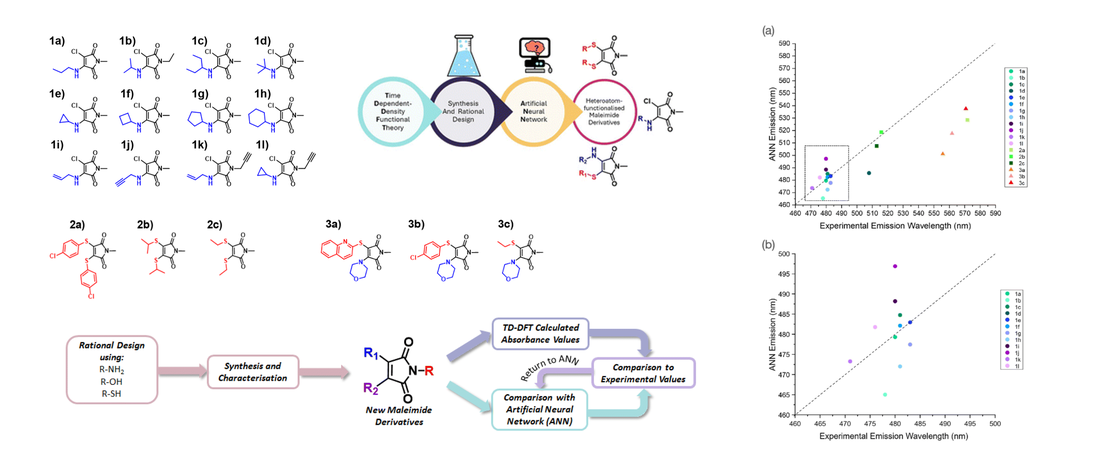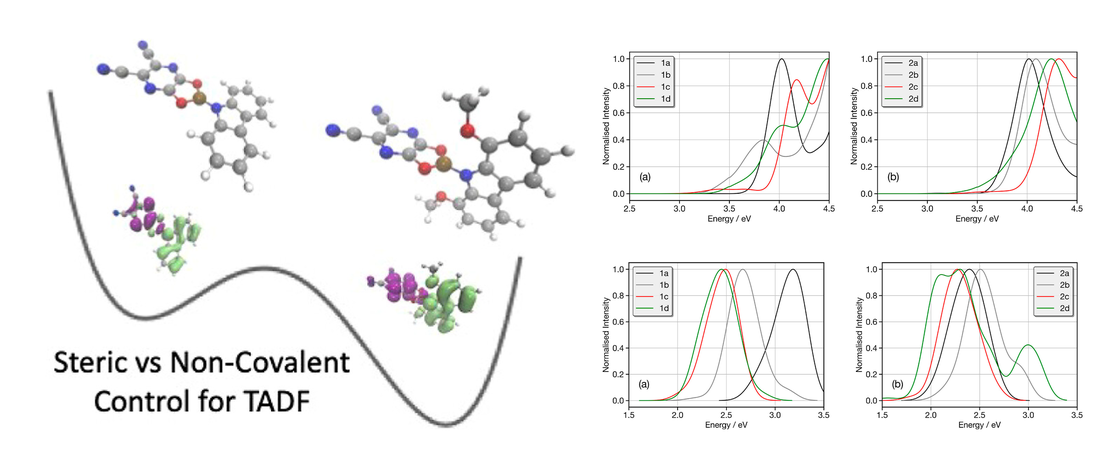
Conformational Control of Donor–Acceptor Molecules Using Non-covalent Interactions
- Shawana Ahmad, Julien Eng and Thomas J. Penfold
- Publication
- September 17, 2024
Abstract:
Controlling the architecture of organic molecules is an important aspect in tuning the functional properties of components in organic electronics. For purely organic thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) molecules, design is focused upon orthogonality orientated donor and acceptor units. In these systems, the rotational dynamics around the donor and acceptor bond has been shown to be critical for activating TADF; however, too much conformational freedom can increase the non-radiative rate, leading to a large energy dispersion of the emitting states and conformers, which do not exhibit TADF. To date, control of the motion around the D–A bond has focused upon steric hindrance. In this work, we computationally investigate eight proposed donor–acceptor molecules, exhibiting a B–N bond between the donor and acceptor. We compare the effect of steric hindrance and noncovalent interactions, achieved using oxygen (sulfur) boron heteroatom interactions, in exerting fine conformational control of the excited state dynamics. This work reveals the potential for judiciously chosen noncovalent interactions to strongly influence the functional properties of TADF emitters, including the accessible conformers and the energy dispersion associated with the charge transfer states.
Additional Resources
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpca.4c03711
Bibtex:
@article{ahm24conformational,
author = {Ahmad, Shawana and Eng, Julien and Penfold, Thomas J.},
title = {Conformational Control of Donor–Acceptor Molecules Using Non-covalent Interactions},
journal = {The Journal of Physical Chemistry A},
volume = {128},
number = {38},
pages = {8035-8044},
year = {2024},
doi = {10.1021/acs.jpca.4c03711},
note ={PMID: 39287185},
URL = {https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpca.4c03711},
eprint = {https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpca.4c03711},
}