Perspective: Vibronic Coupling Potentials for Trajectory-Based Excited-State Dynamics
- Sandra Gómez, Patricia Vindel-Zandbergen, Dilara Farkhutdinova, and Leticia González
- Publication , Perspective , Project partner
- September 11, 2025
Abstract:
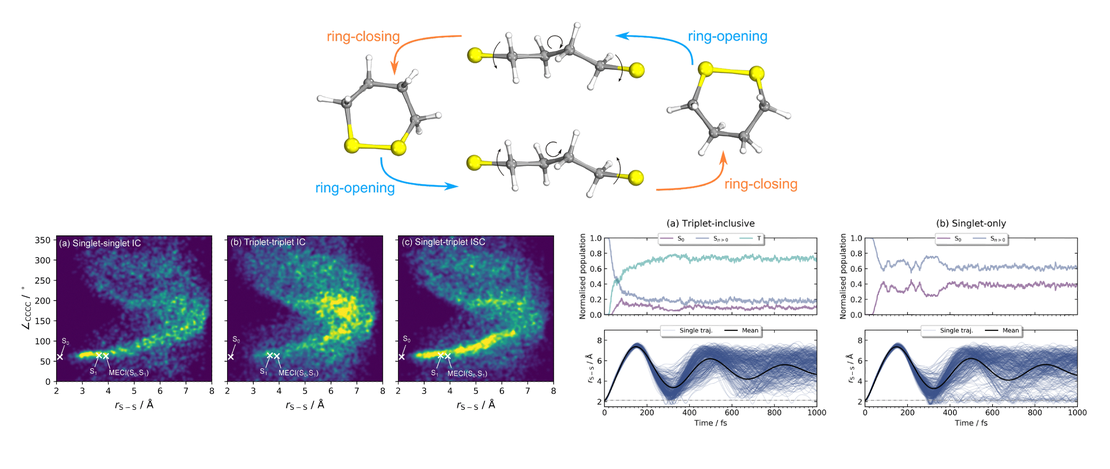
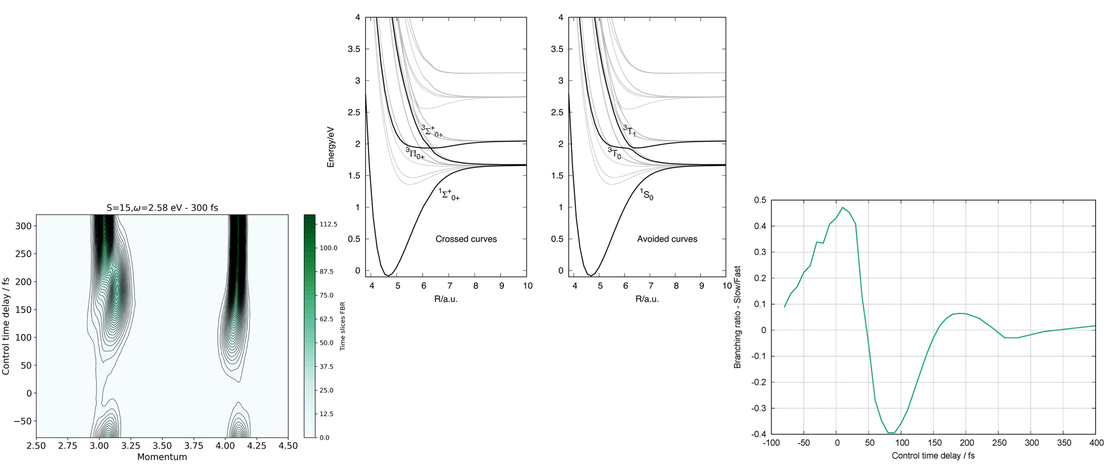
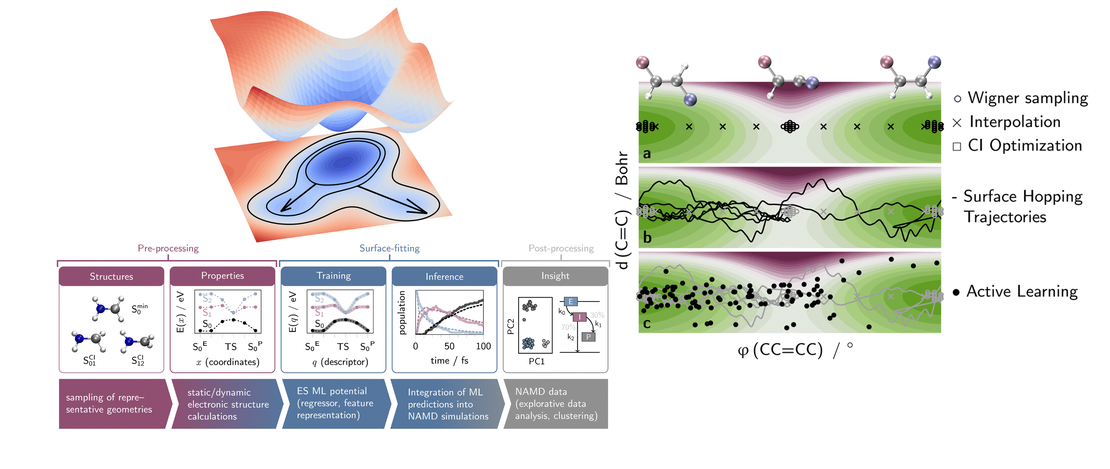
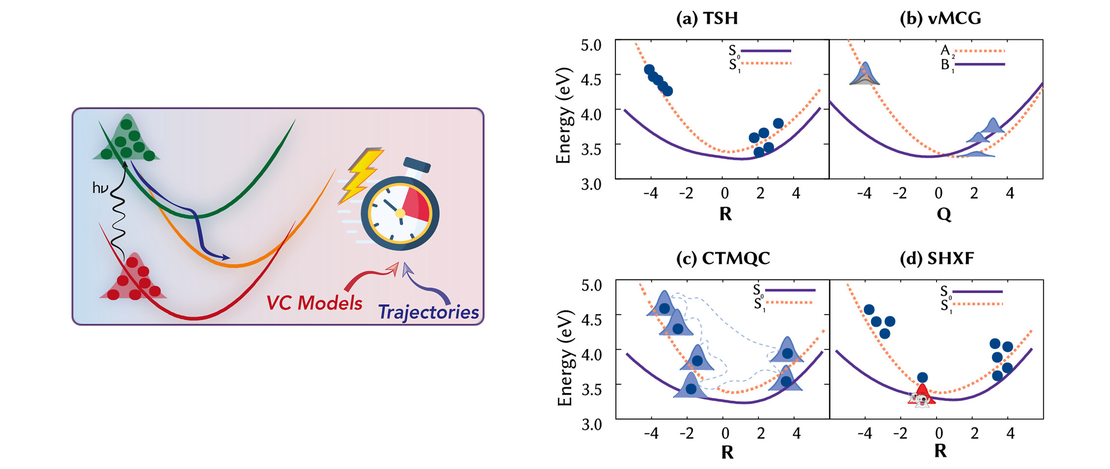
This Perspective reviews the use of vibronic coupling (VC) potentials in trajectory-based excited-state dynamics simulations. Originally developed to provide simplified yet physically grounded representations of nonadiabatic interactions, VC models - particularly their linear version (LVC) - have facilitated extensive investigations of photophysical and photochemical processes, in both molecular and condensed-phase systems. By effectively capturing the coupling between electronic and vibrational motions, VC models enable efficient dynamical simulations, making it feasible to investigate larger and more complex systems, for longer time scales or relying on potential energy surfaces calculated with high levels of theory. These models provide valuable insights into energy and charge transfer mechanisms following photoexcitation, shedding light on excited-state lifetimes and intricate relaxation pathways. Here, we discuss their integration with three trajectory-based computational families of methods: surface hopping, variational multiconfigurational Gaussian, and exact-factorization-derived approaches. We showcase how VC models have helped uncovering key mechanistic insights, including state-specific intersystem crossing pathways and vibrational mode selectivity. As the field progresses, VC-based approaches are expected to be increasingly combined with machine learning, anharmonic corrections, and hybrid LVC/MM frameworks, broadening their applicability to complex, flexible, and solvated environments. We highlight the advantages of VC-based potentials for trajectory-based simulations, emphasizing their computational efficiency and usefulness for benchmarking and exploring photophysical processes in molecular systems.
Additional Resources
DOI:
Quick Ref:
J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2025, 21, 8634−8649